When it comes to insulating a building, there are several options to choose from. Two of the most popular materials are spray foam insulation and fiberglass insulation. Both have unique benefits and drawbacks, and the right choice for your project will depend on your specific needs and goals. In this article, we’ll compare spray foam insulation and fiberglass insulation to help you make an informed decision.
Spray Foam Insulation
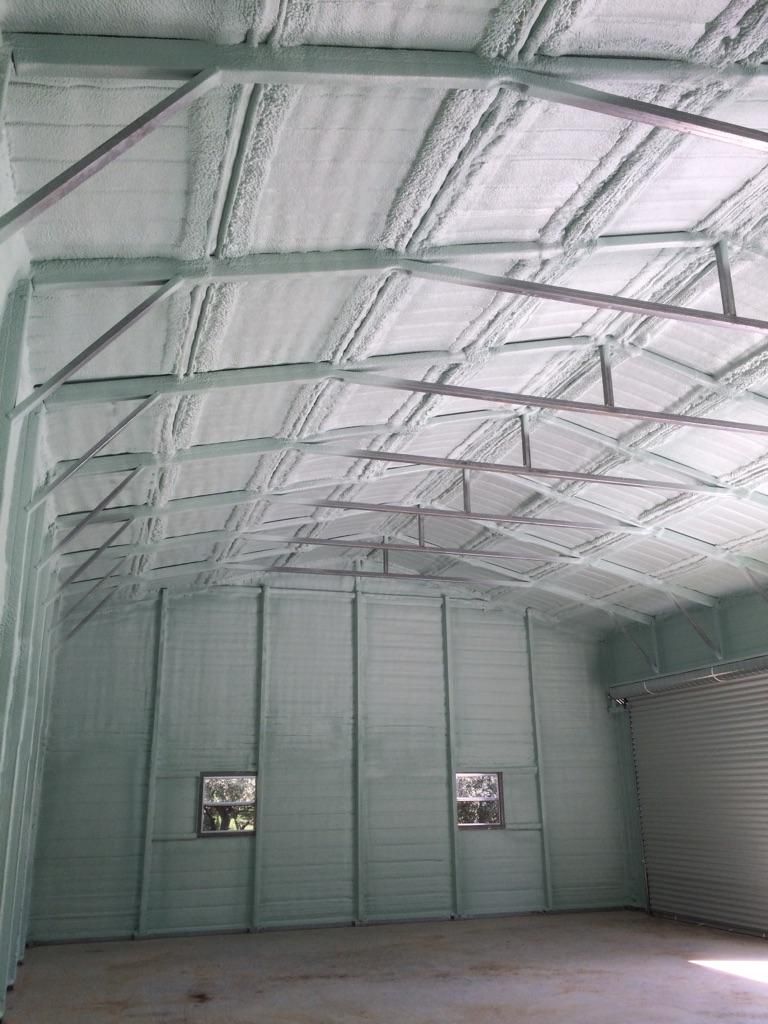
Spray foam insulation is a versatile and effective solution for insulating buildings of all types and sizes. It is applied as a liquid and expands to fill gaps and cracks in the building envelope, creating an airtight seal. This makes it an excellent choice for sealing hard-to-reach areas and preventing air leakage.
One of the primary benefits of spray foam insulation is its ability to save energy. By sealing gaps and cracks in the building envelope, spray foam insulation helps to maintain a consistent temperature inside the building, reducing the need for heating and cooling systems to work as hard. This can significantly reduce energy consumption and lower energy bills.
In addition to its insulating properties, spray foam insulation also has a high R-value, which measures its ability to resist heat transfer. The higher the R-value, the more effective the insulation. Spray foam insulation typically has an R-value of 6.0 to 7.0 per inch, making it one of the highest-performing insulation materials on the market.
Spray foam insulation is also highly durable. It is resistant to water, mold, and pests and does not settle or sag over time like other insulation materials. This makes it an excellent long-term investment for any building.
One potential drawback of spray foam insulation is the cost. It is generally more expensive than other types of insulation, although its energy-saving properties can help offset the initial cost over time.
Fiberglass Insulation
Fiberglass insulation is a popular choice for insulating buildings due to its low cost and ease of installation. It is made from fine strands of glass woven together and then bound with a resin to create a lightweight, flexible material. Fiberglass insulation is available in various forms, including rolls, batts, and loose-fill.
One of the primary benefits of fiberglass insulation is its low cost. It is generally less expensive than other types of insulation, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious homeowners and businesses.
Fiberglass insulation also has a relatively high R-value, typically 2.2 to 2.7 per inch. While this is lower than the R-value of spray foam insulation, it is still an effective insulator and can help reduce energy consumption and lower energy bills.
One potential drawback of fiberglass insulation is its durability. It can settle or sag over time, reducing its effectiveness as an insulator. It is also prone to moisture absorption, which can lead to the growth of mold and other pests.
Which is Better?
Both spray foam insulation and fiberglass insulation are practical options for insulating buildings. Spray foam insulation is more expensive but offers higher energy savings and greater durability. Fiberglass insulation is less expensive but has a lower R-value and may not be as durable. The right choice for your project will depend on your specific needs and goals. Consider the benefits and drawbacks of both types of insulation and choose the option that best meets your needs and budget.